Definition
Osteochondrosis dissecans, or OCD occurs when a piece of cartilage becomes loose or pulls away from the surface of a joint causing pain and inflammation. It usually occurs during the process of endochondral ossification as the dog is growing and it’s commonly seen in the shoulder, elbow and hock.
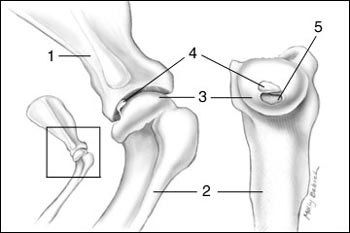 In fast growing breeds, the rapid cartilage growth can over accelerate and out strip its blood supply resulting in the retention of excessive cartilage which may develop cracks in its important cushioning and weight bearing surface. Over time a section of the joint cartilage can separate from the bone creating a flap which can vary in size. This flap irritates the joint and surrounding tissue leading to pain and inflammation, excessive calcium deposits and the early onset of arthritis.
In fast growing breeds, the rapid cartilage growth can over accelerate and out strip its blood supply resulting in the retention of excessive cartilage which may develop cracks in its important cushioning and weight bearing surface. Over time a section of the joint cartilage can separate from the bone creating a flap which can vary in size. This flap irritates the joint and surrounding tissue leading to pain and inflammation, excessive calcium deposits and the early onset of arthritis.
Causes
- Excessive exercise as a puppy
- Fast growing breeds
- Genetics
- Harmful activities of daily living e.g. ball chasing, living on laminate/slippy floors
- Physical impact or trauma e.g. a fall or collision
- Body size and weight
- Nutritional deficiency
- Hormonal imbalances
- Body size and weight, dietary or nutritional deficiency during the first few months of life, hormonal imbalances and joint trauma are all factors which can increase the risk of developing OCD.
Signs / Symptoms
- Lameness, may be mild initially
- Uneven weight bearing of the limbs
- Scuffing of nails on the affected leg as flexion through the elbow is reduced
- Muscle atrophy
- Worse after exercise
- Swelling of joints
- Reluctant to flex or extend affected joint on manipulation
Dogs At Risk
Different breeds appear to be predisposed to developing the condition in different joints. For example, the shoulder joint is most commonly affected in Border Collies, Great Danes and Irish Wolfhounds.
OCD in general is much more prevalent in Labradors, Golden Retrievers, German Shepherds, Rottweilers, Great Danes, Newfoundlands, Bernese Mountain Dogs, English Setters, and Old English Sheepdogs.
It is uncommon in small breeds.
Benefits Of Massage
- Quicker post surgical recovery (if an operation is required)
- Reduces recuperation time by minimising pain and aiding comfort
- Helps improves mobility
- Develops and maintains muscles tone
- Encourages weight bearing equally on all 4 limbs
- Helps to strengthen the affected leg and restore the muscle tone
To find a therapist in your area, check out the “Find a Therapist” page